Alcohol Induced Pseudo Cushing Syndrome
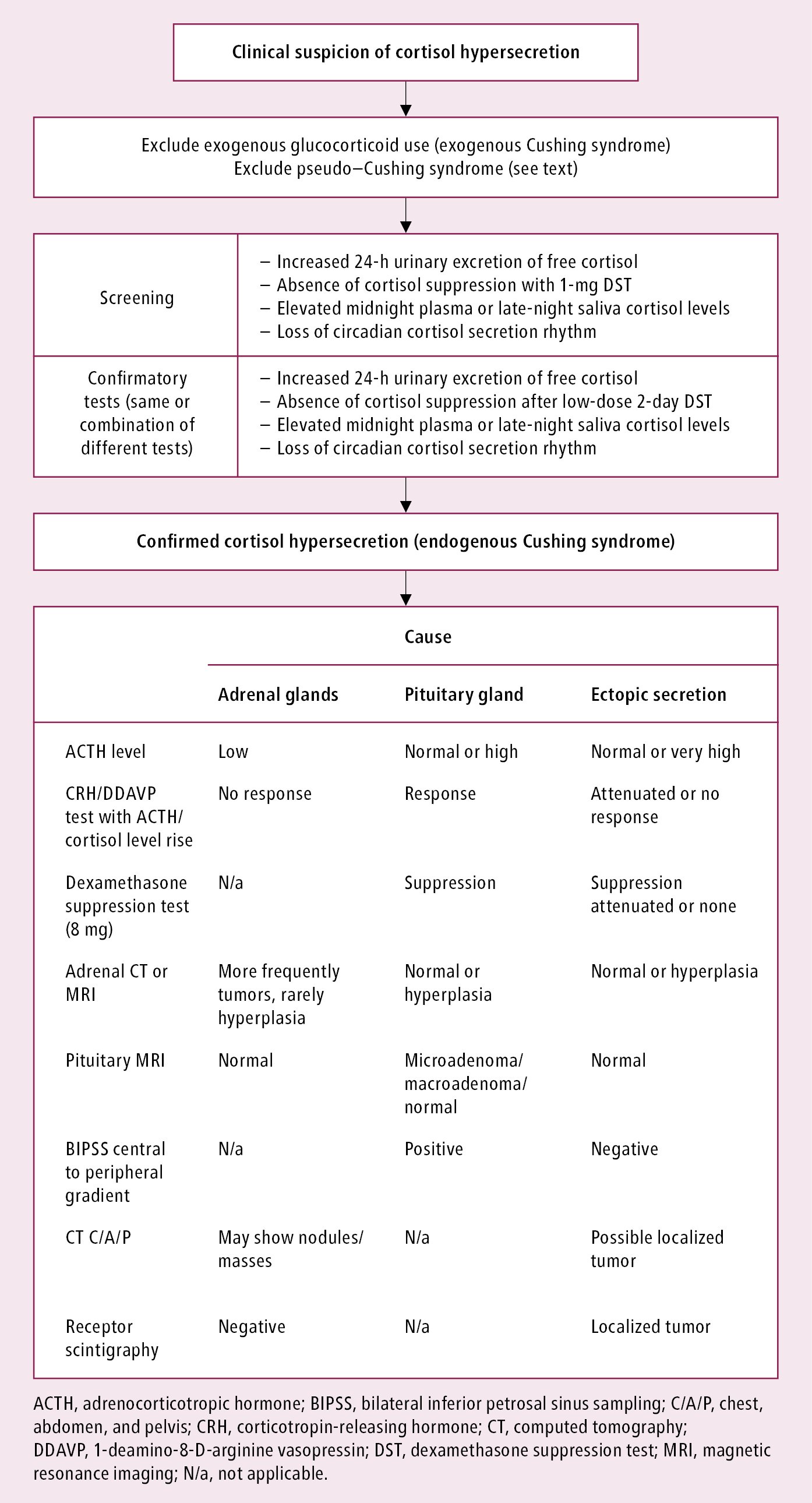
Alcohol induced pseudo cushing syndrome. Patience is also needed. There is no clear definition for the alcohol-induced pseudo-Cushing state and hitherto studies fail to provide clues to differentiate between pseudo-Cushing and Cushings syndrome. A challenge in clinical endocrinology is the distinction between Cushings disease Cushings syndrome dependent by adrenocorticotrophic hormone ACTH-secreting tumours of pituitary origin and alcohol-dependent pseudo-Cushings syndrome.
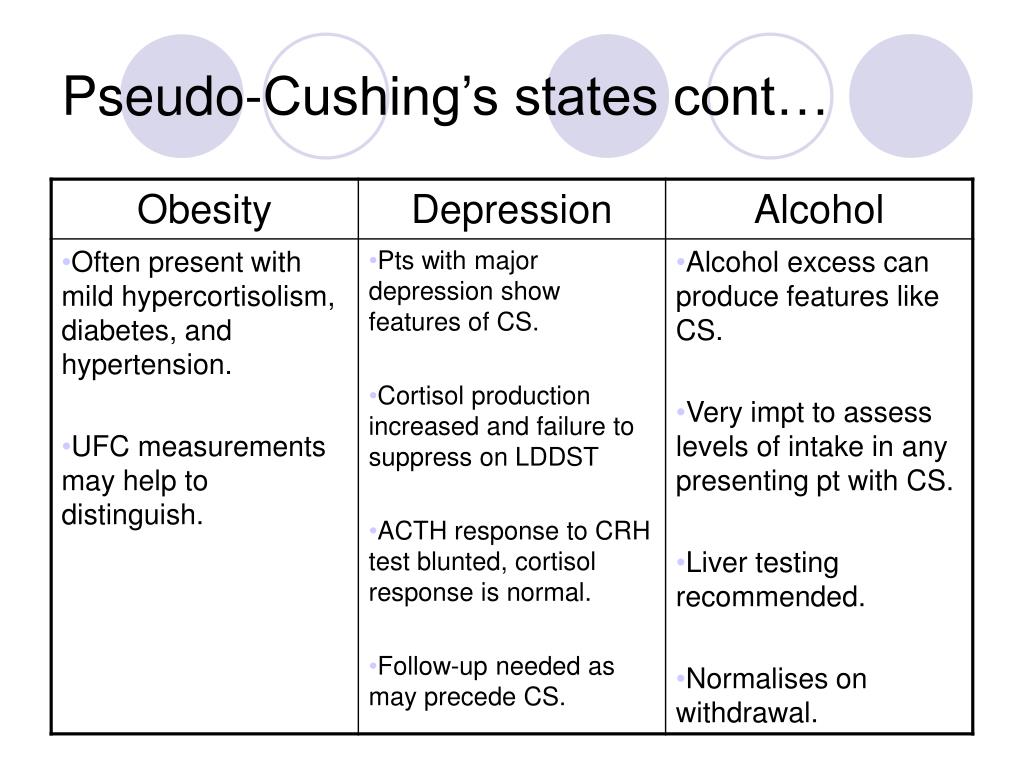
In 4 patients corticosteroid hypersecretion associated with excessive intake of alcohol led initially to an erroneous diagnosis of Cushings syndrome. 4 suggest the CRH test after administration of low-dose dexamethasone 2 mgday for 2 days to separate these two syndromes. Smals A Kloppenborg P.
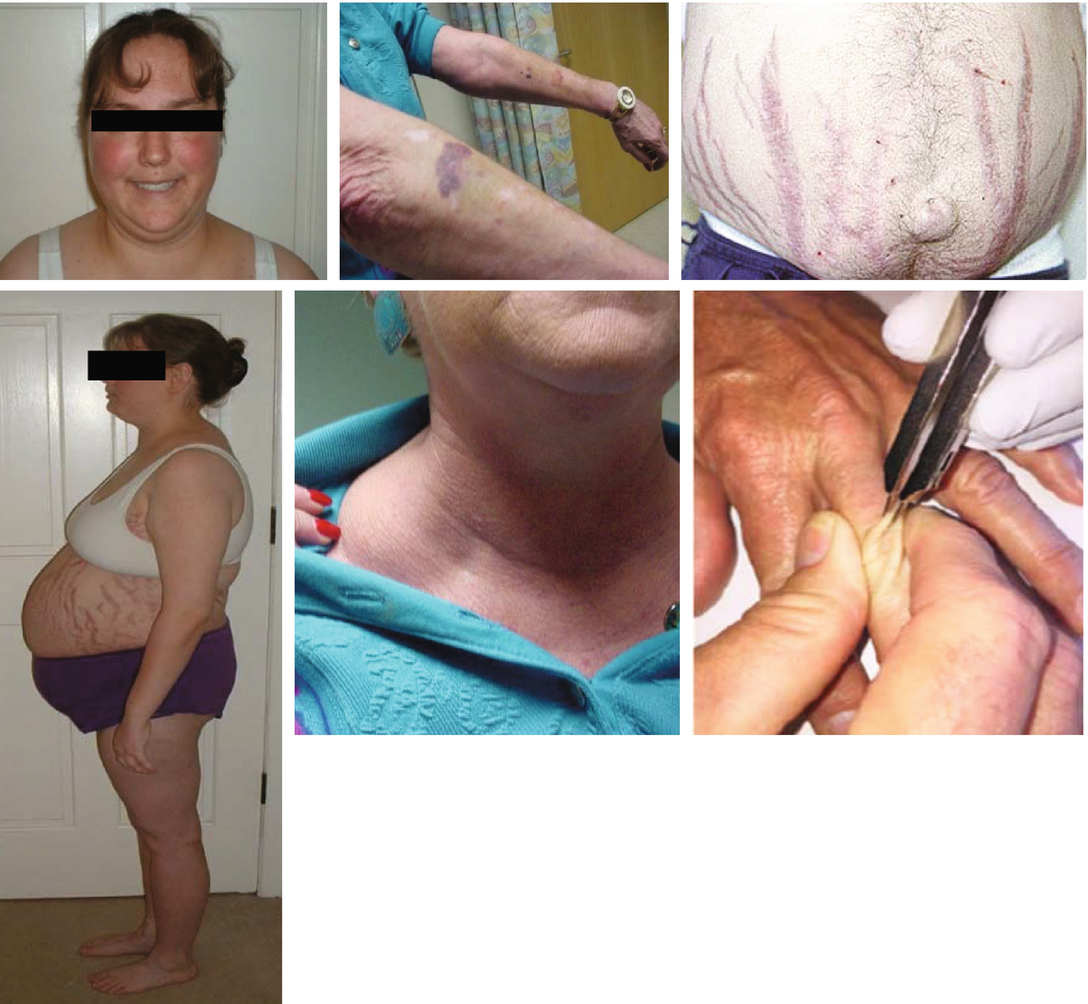
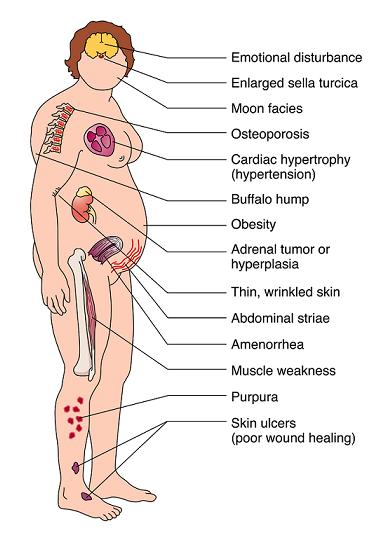
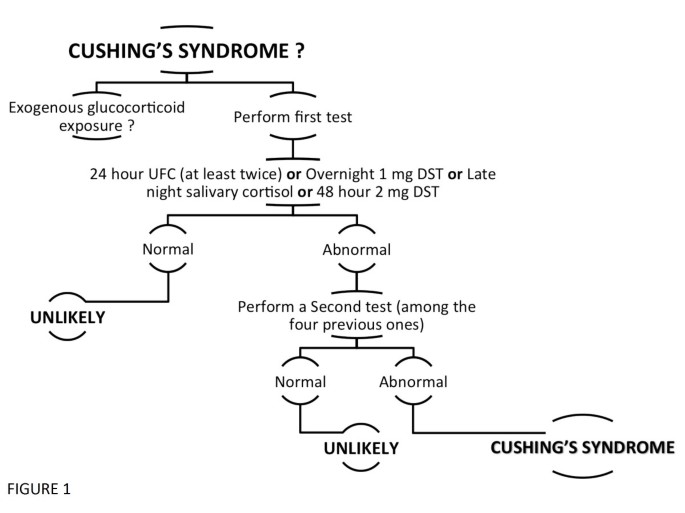
Chronic alcoholism and associated magnesium and potassium deficiencies may cause a condition called pseudo-Cushings syndrome a recent case report from Japan shows. To prevent this frustration working closely with a good Endocrinologist who sees many patients with Cushings syndrome is needed. The name alcohol- induced pseudo-Cushings syndrome was coined in 19761 and other cases soon followed2 Apart from the clinical features the patients have one or more suggestive biochemical abnormalities-eg increased plasma or urinary cortisol reduced circadian rhythm of plasma cortisol or impaired response in an overnight or 48 h low-dose dexamethasone suppression test.
Only cessation of alcohol can normalise biochemical abnormalities and regress hypercortisolic symptoms. It is generally transient and resolved after approximately 4weeks of alcohol abstinence 1 2 4 Therefore in contrast to Cushings disease pseudoCushings syndrome does not require therapeutic attention from an endocrine point of view. Chronic alcoholism 3 A particular type of hypercortisolism presenting during the above conditions named functional hypercortisolism is caused by chronic activation of.
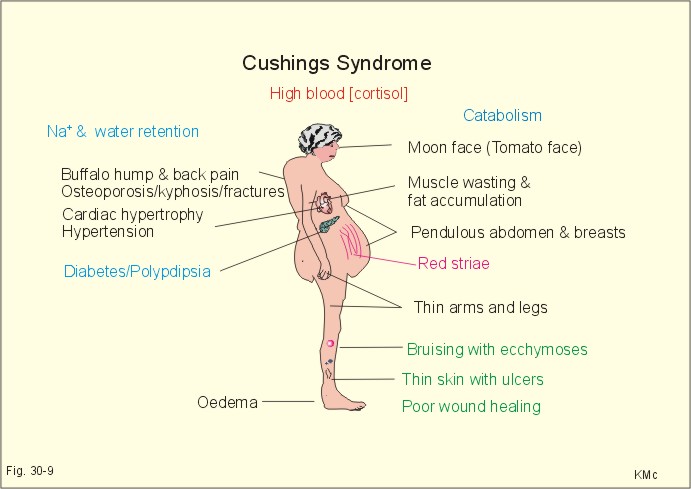
Alcohol-induced pseudo-Cushings syndrome is a disorder in which patients exhibit clinical andor biochemical features similar to those in patients with Cushings syndrome but these features related to alcohol abuse may be transient and resolve during abstinence from alcohol. This is thought to occur due to an effect on the liver which decreases the clearance of cortisol resulting in excessive urinary cortisol and symptoms. Ence of Cushings disease.
This condition is called alcoholinduced pseudoCushing syndrome. An insufficient suppression of plasma cortisol to the overnight administration of 1 mg of dexamethasone was. If diagnostic errors are to be avoided a history of alcohol intake should always be sought in a patient in whom the diagnosis of Cushings syndrome is entertained.
Alcohol-induced pseudo-Cushings syndrome 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 BillableSpecific Code E244 is a billablespecific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Alcohol-induced pseudo-Cushings syndrome is indistinguishable from true Cushings syndrome although in the former less signs and symptoms seem to be present 3.
This condition is called alcoholinduced pseudoCushing syndrome.
This is thought to occur due to an effect on the liver which decreases the clearance of cortisol resulting in excessive urinary cortisol and symptoms. The research Hypokalemia associated with pseudo-Cushings syndrome and magnesium deficiency induced by chronic alcohol abuse was published in the journal CEN Case Reports. Ence of Cushings disease. One cause of developing symptoms and signs of Cushings is excessive alcohol intake. Smals A Kloppenborg P. JAMA 2421640-1643 1979 RECENTLY several cases of alcohol-induced pseudo-Cushings syndrome have been reported13 The most im portant common characteristics of the nine patients described in these. An insufficient suppression of plasma cortisol to the overnight administration of 1 mg of dexamethasone was. Patience is also needed. This is called pseudo-Cushings.
The name alcohol- induced pseudo-Cushings syndrome was coined in 19761 and other cases soon followed2 Apart from the clinical features the patients have one or more suggestive biochemical abnormalities-eg increased plasma or urinary cortisol reduced circadian rhythm of plasma cortisol or impaired response in an overnight or 48 h low-dose dexamethasone suppression test. Patience is also needed. One cause of developing symptoms and signs of Cushings is excessive alcohol intake. The name alcohol- induced pseudo-Cushings syndrome was coined in 19761 and other cases soon followed2 Apart from the clinical features the patients have one or more suggestive biochemical abnormalities-eg increased plasma or urinary cortisol reduced circadian rhythm of plasma cortisol or impaired response in an overnight or 48 h low-dose dexamethasone suppression test. We describe the clinical and biochemical characteristics of alcohol-induced pseudo-Cushings syndrome in two patients with signs and symptoms of Cushings syndrome and slight disturbances in liver function. In most previous reports of alcohol-induced pseudo-Cushings syndrome detailed endocrinologic data supporting a diagnosis of Cushings syndrome. There is no clear definition for the alcohol-induced pseudo-Cushing state and hitherto studies fail to provide clues to differentiate between pseudo-Cushing and Cushings syndrome.




























Post a Comment for "Alcohol Induced Pseudo Cushing Syndrome"