Chronic Kidney Disease Fluid Intake
Chronic kidney disease fluid intake. Stage four kidney disease is described by the reduced kidney function between 29-15 mlmin GFR that raises the chances of getting prone to other complications like heart failure kidney failure nervous breakdown etc. In fact according to the classical model under normal conditions high salt intake temporarily increases plasma sodium level which is soon buffered by movement of water from the. Enough quantities of water can help in binding the formation of crystals in kidneys and dissolves antibiotics to prevent UTIs.
The reason that physicians tend to recommend such an increased fluid intake is difficult to understand. Drinking 4 to 6 liters a day can lead to the healthy functioning of kidneys. Nutrition in chronic kidney disease.
I recommend 60-80 ounces of water per day depending on your body weight. Fatigue or weakness due to reduced production of red blood cells. A scientific basis does not exist.
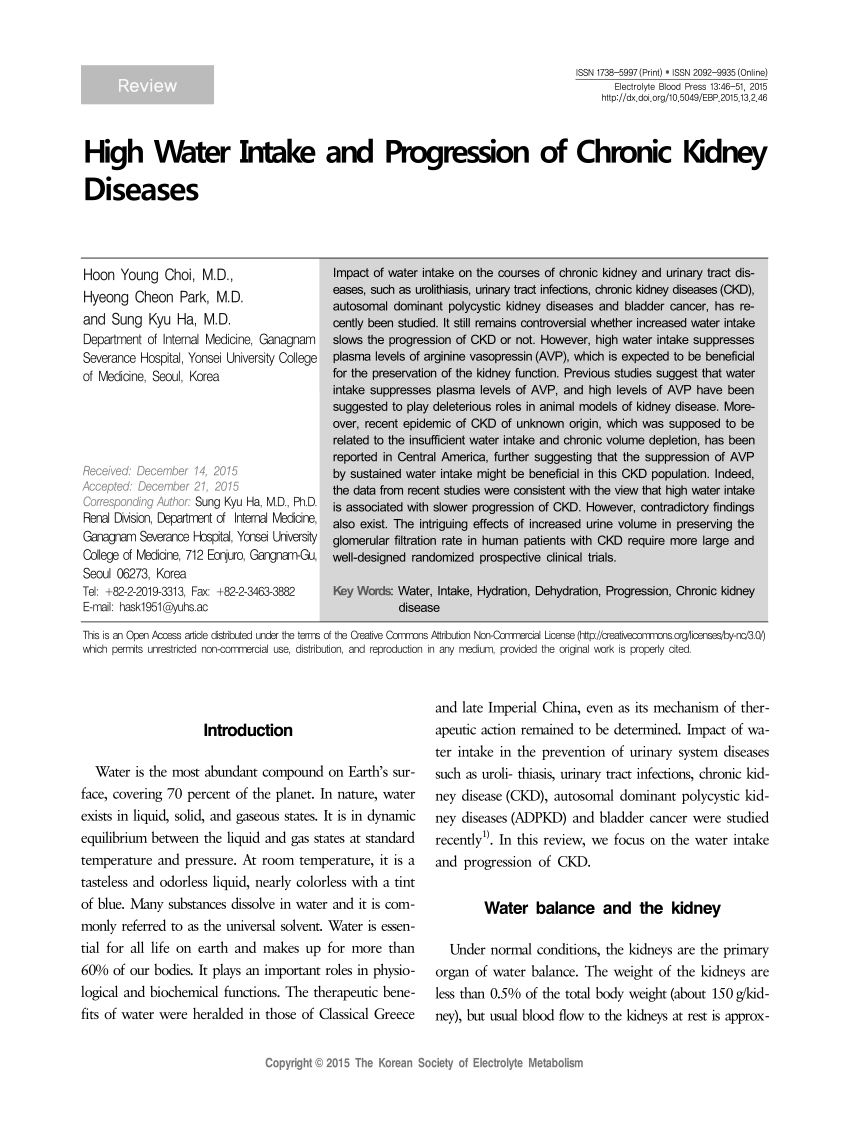
Women should aim to drink eight 200ml glasses of fluid a day. Kidney Stones If you have kidney stones your doctor may be telling you to drink more fluids to prevent kidney stone formation. We have identified 21 antecedents in the literature for the fluid overload concept in Chronic Kidney Disease patients undergoing dialysis therapy with emphasis on excess fluid intake high sodium diet decreased glomerular filtration rate difficulty in adhering to fluid restrictions and diabetes.
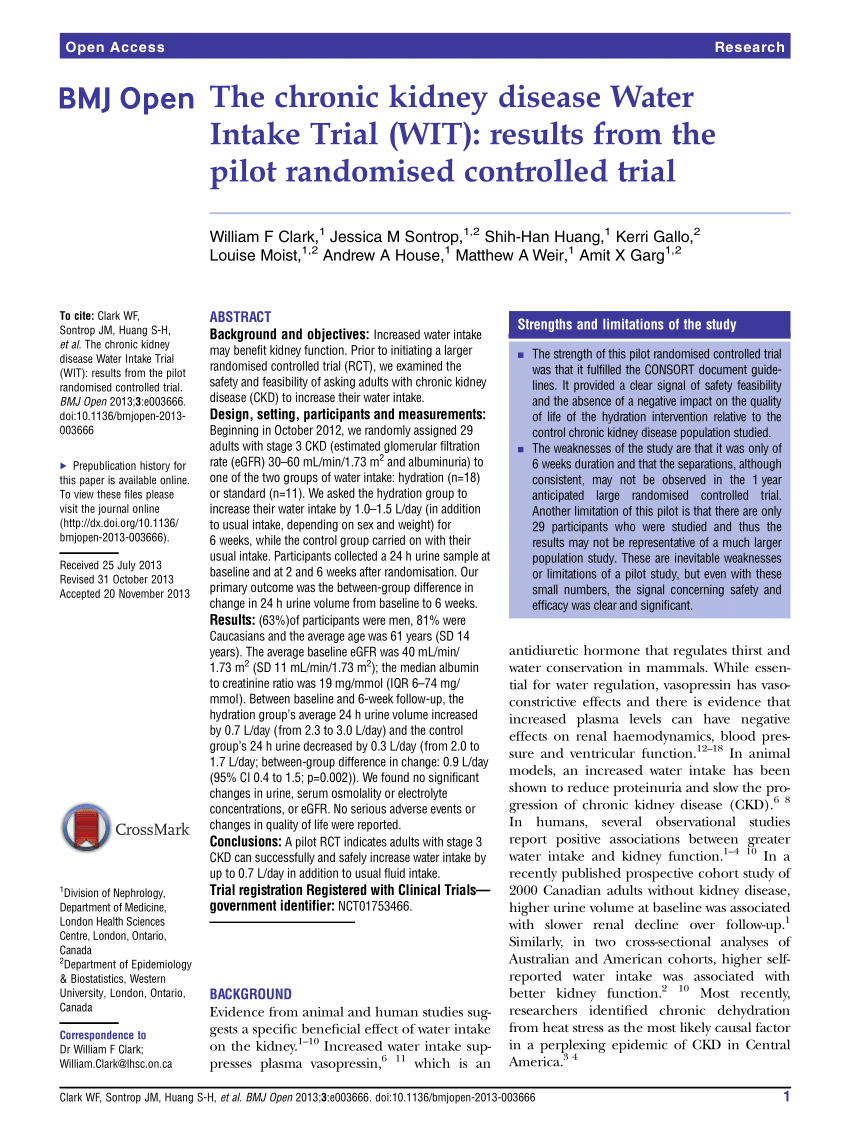
For people in the later stages of chronic kidney disease CKD these normal amounts of fluid can build up in the body and be dangerous. Neither total water intake nor urine volume was associated with either kidney outcome. Fluid control for those on hemodialysis.
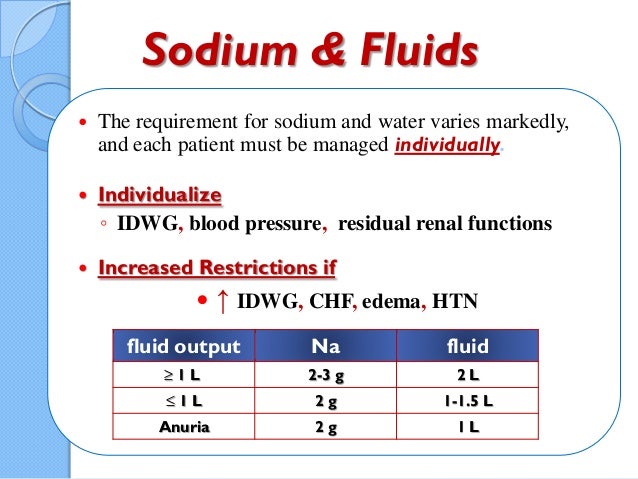
Patients with chronic kidney failure commonly are advised to maintain a generous fluid intake. Despite promising role of diuretics to manage fluid overload among chronic kidney disease CKD patients their use is associated with adverse renal outcomes. At the early stages of chronic kidney disease kidney patients are advised to drink more water so that it can help in the right removal of toxins.
Diet in Chronic Kidney Disease Salts electrolytes Sodium Potassium Phosphate Protein Fluid intake Vitamins Iron Maintaining a healthy weight Dialysis. There are various symptoms that are associated with Stage 4 chronic kidney disease.
Salt and water retention play a key role for development of hypertension in CKD.
The bottom line is that kidneys dont need to cleansed -- either by increasing their water intake or by using products found on the Internet. Fluid control for those on hemodialysis. Stage four kidney disease is described by the reduced kidney function between 29-15 mlmin GFR that raises the chances of getting prone to other complications like heart failure kidney failure nervous breakdown etc. In fact according to the classical model under normal conditions high salt intake temporarily increases plasma sodium level which is soon buffered by movement of water from the. Fatigue or weakness due to reduced production of red blood cells. It is not as efficient as a human kidney so people with kidney failure usually need to restrict their intake of fluid and certain foods. Kidney Stones If you have kidney stones your doctor may be telling you to drink more fluids to prevent kidney stone formation. Median urine volume was 19 16-24 L24 h and mean eUosm 374 104 mosmL. Men should aim to drink ten 200ml glasses of fluid a day.
Despite promising role of diuretics to manage fluid overload among chronic kidney disease CKD patients their use is associated with adverse renal outcomes. In fact according to the classical model under normal conditions high salt intake temporarily increases plasma sodium level which is soon buffered by movement of water from the. For people in the later stages of chronic kidney disease CKD these normal amounts of fluid can build up in the body and be dangerous. 16-26 L total water and 15 1-17 L plain water. A scientific basis does not exist. High Water Intake and Progression of Chronic Kidney Diseases. Salt and water retention play a key role for development of hypertension in CKD.




































Post a Comment for "Chronic Kidney Disease Fluid Intake"