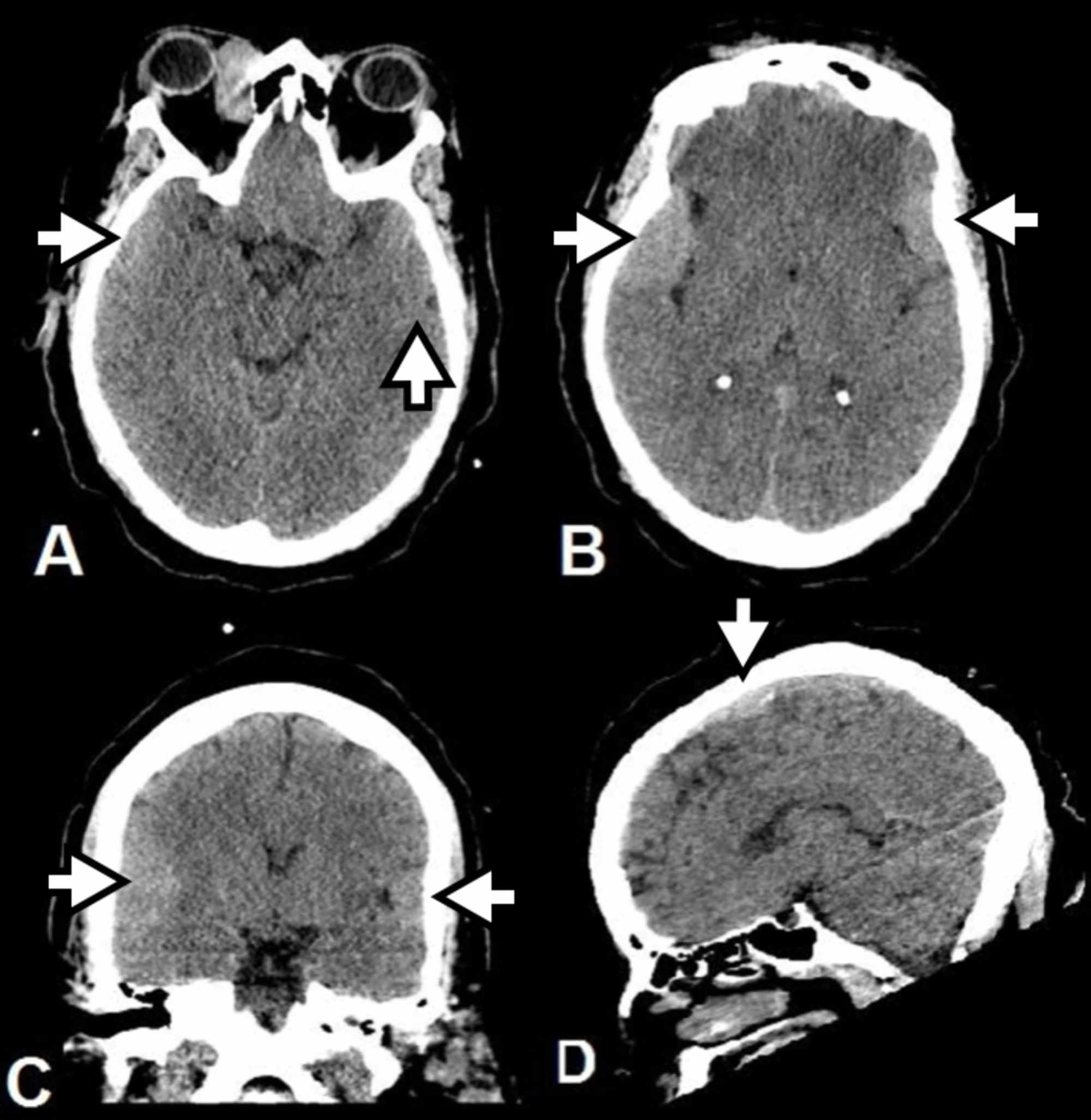
Rosai Dorfman Disease Brain
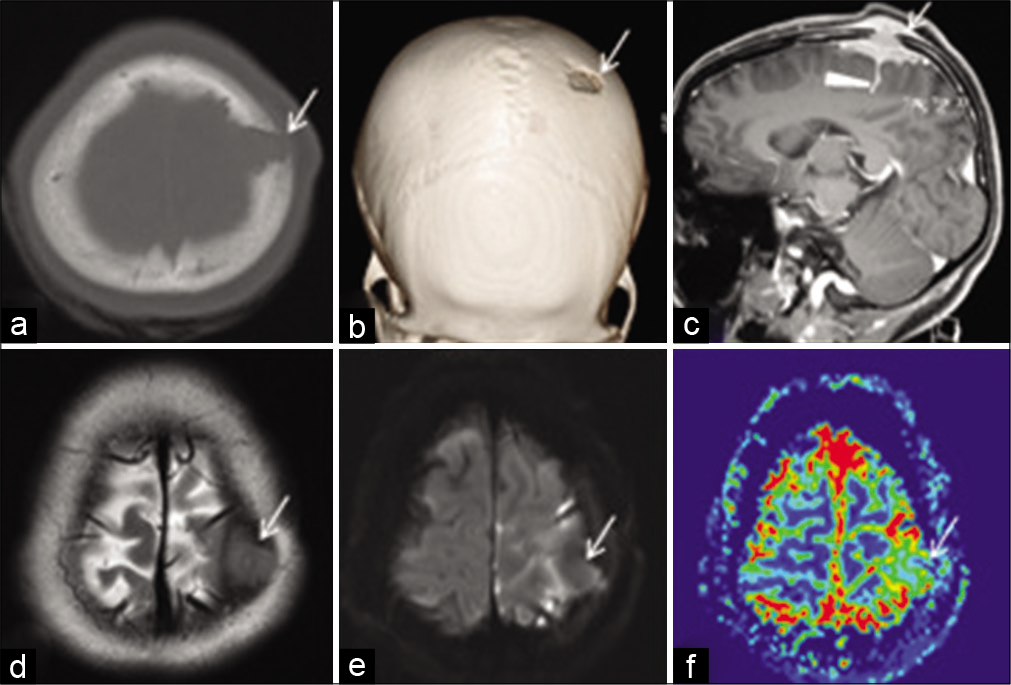
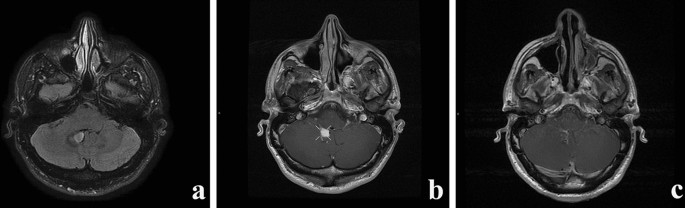
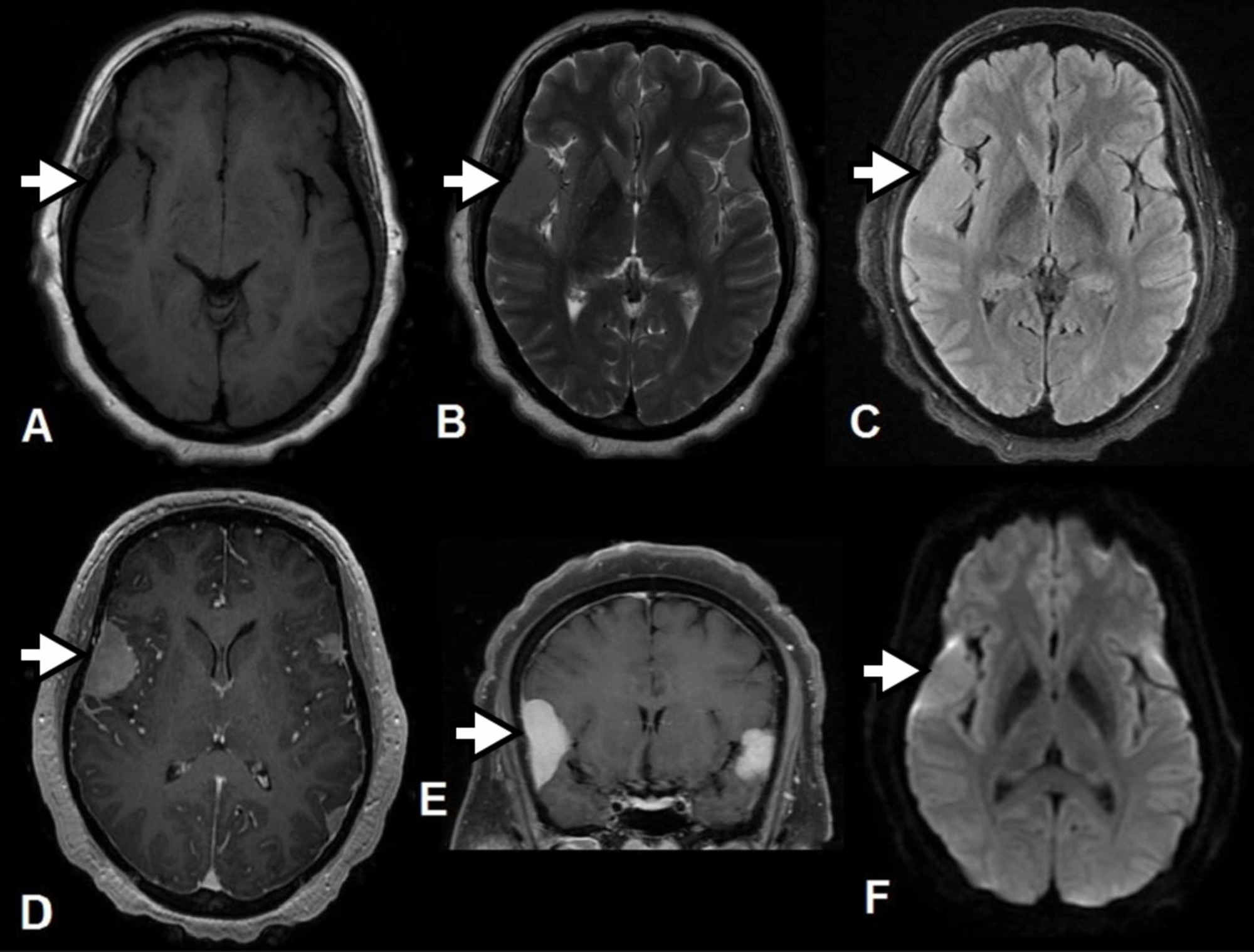
Rosai dorfman disease brain. The phenotype of Faisalabad histiocytosis overlaps with that of Rosai-Dorfman disease RDD or sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy SHML a histiocytic disorder characterized by painless but protracted lymphadenopathy with lymph node histology showing large histiocytes with voluminous clear cytoplasm rounded nuclei and emperipolesis. Rosai-Dorfman disease sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy was first described in 1969 as a benign proliferative lesion with systemic symptoms and lymphadenopathy 1. Though it can affect almost any organ system involvement of the nervous system is exceedingly rare.
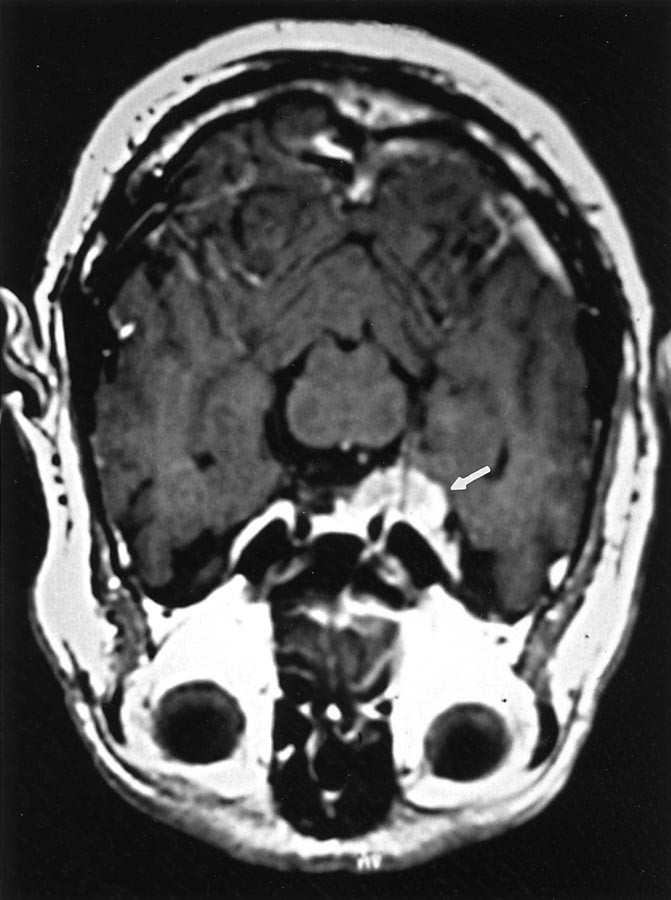
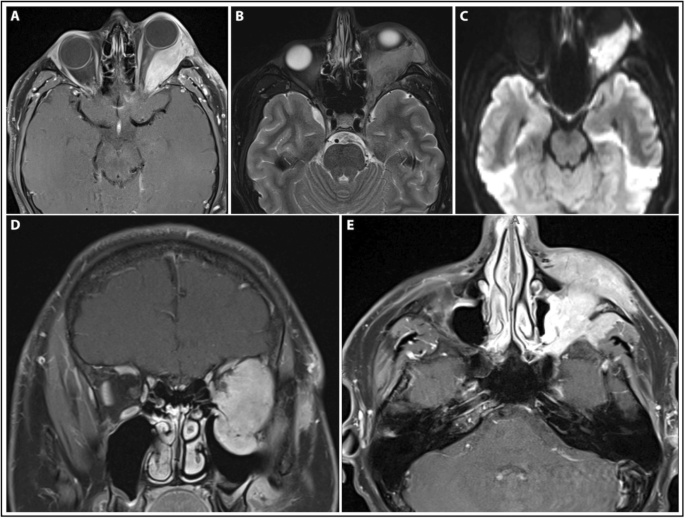
When it does affect the brain spinal cord and meninges it could have profound. Rosai-Dorfman disease RDD first described in 1969 is a disease that occurs when the body produces too many histiocytes in the lymph nodes. Extranodal RDD may occur in 43 of cases 3 4.
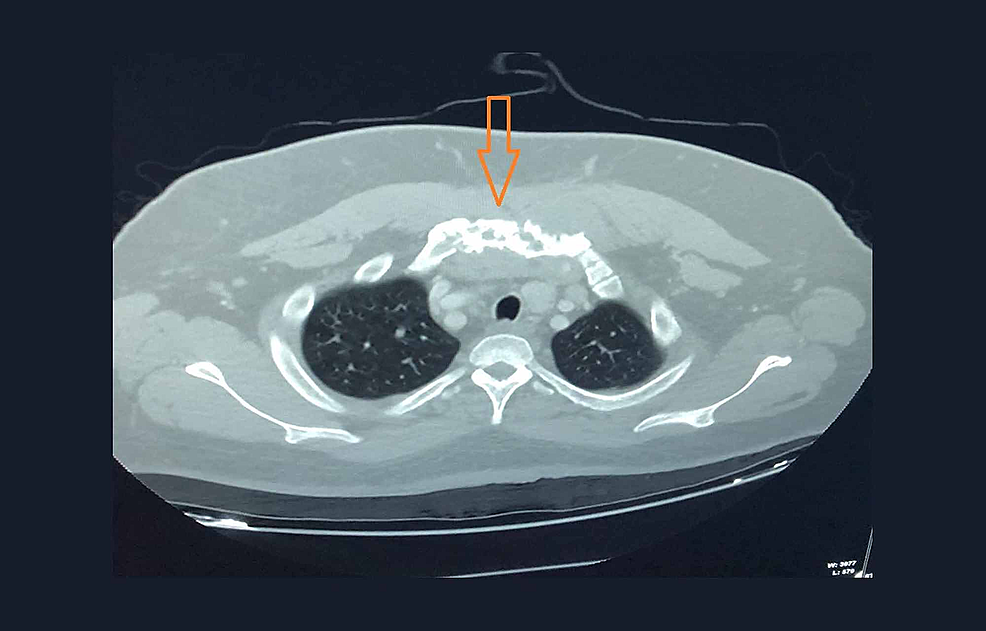
Rosai-Dorfman-Destombes disease RDD is a rare histiocytic disorder described by Destombes in 1965 and later by Rosai and Dorfman in 1969 as sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy and previously classified by the Working Group of the Histiocyte Society of 1987 as a non-Langerhans cell LC histiocytosis. Rosai-Dorfman disease is a rare disorder characterized histologically by lymphatic sinus dilatation due to histiocyte proliferation. Rosai-Dorfman disease commonly involves cervical lymph nodes.
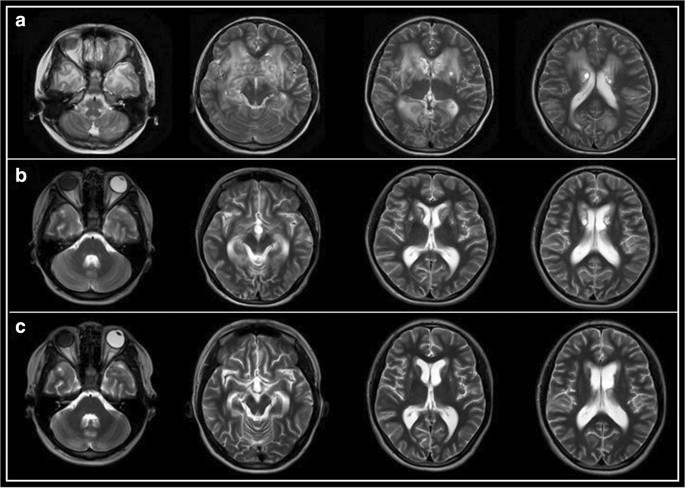
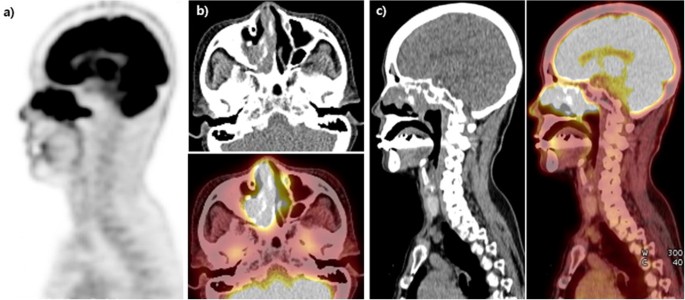
It is a benign disease which is characterized by over-production and accumulation of a specific type of white blood cell histiocyte in the lymph nodes of the body most often those of the neck cervical. It is usually characterized by cervical lymphadenopathy along with systemic features. Our goal was to describe the CT MRI and 18F-FDG FD.
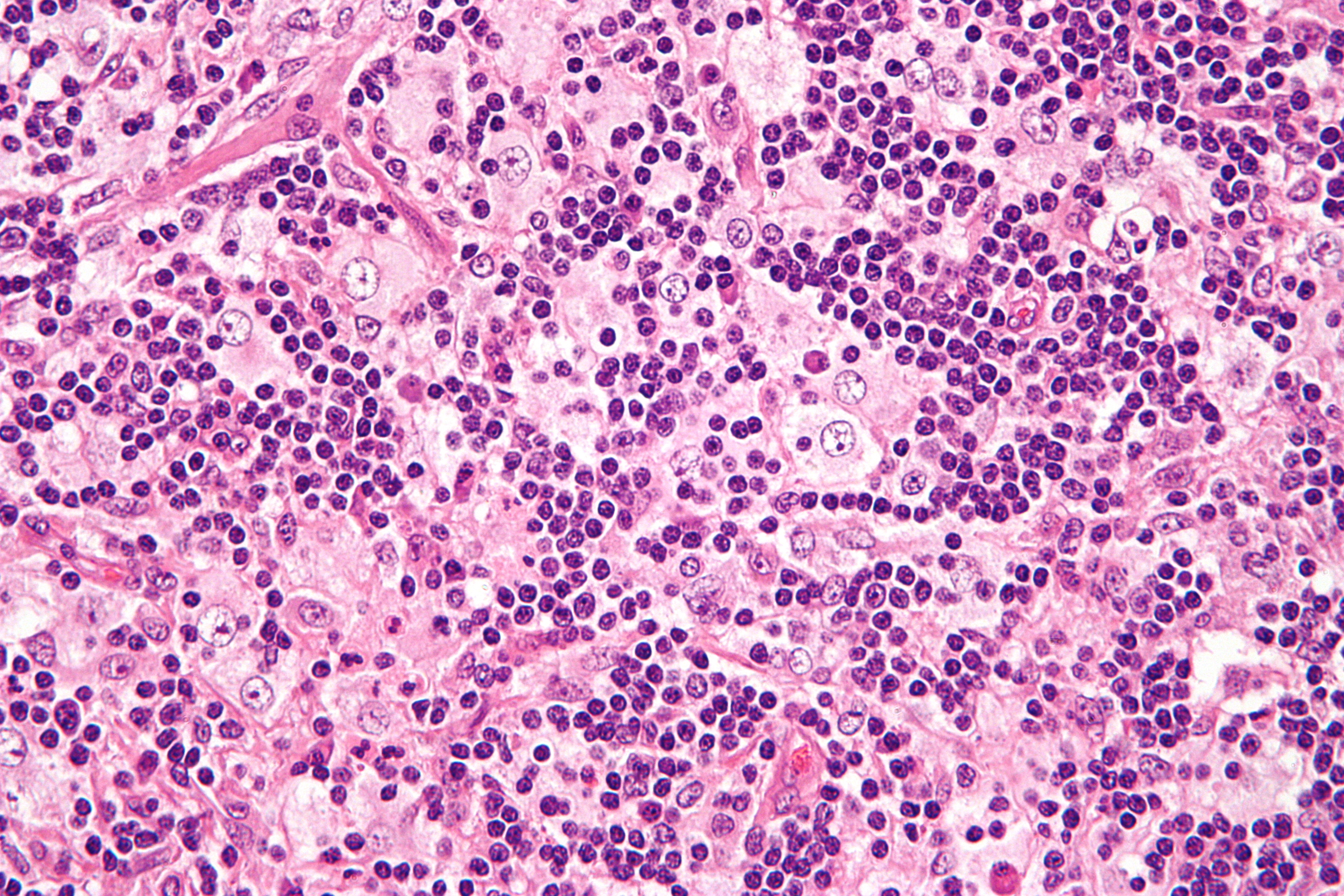
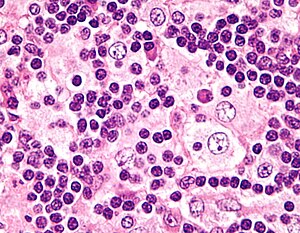
Although it is characterized by unique indeed pathognomonic histopathological cytoarchitecture it may be mistaken for many other neoplastic and inflammatory histioproliferative diseases. Rosai-Dorfman Disease RDD is an idiopathic histiocytic proliferation affecting lymph nodes. It occurs more often in children and young adults and shows a mild male sex predilection 2.
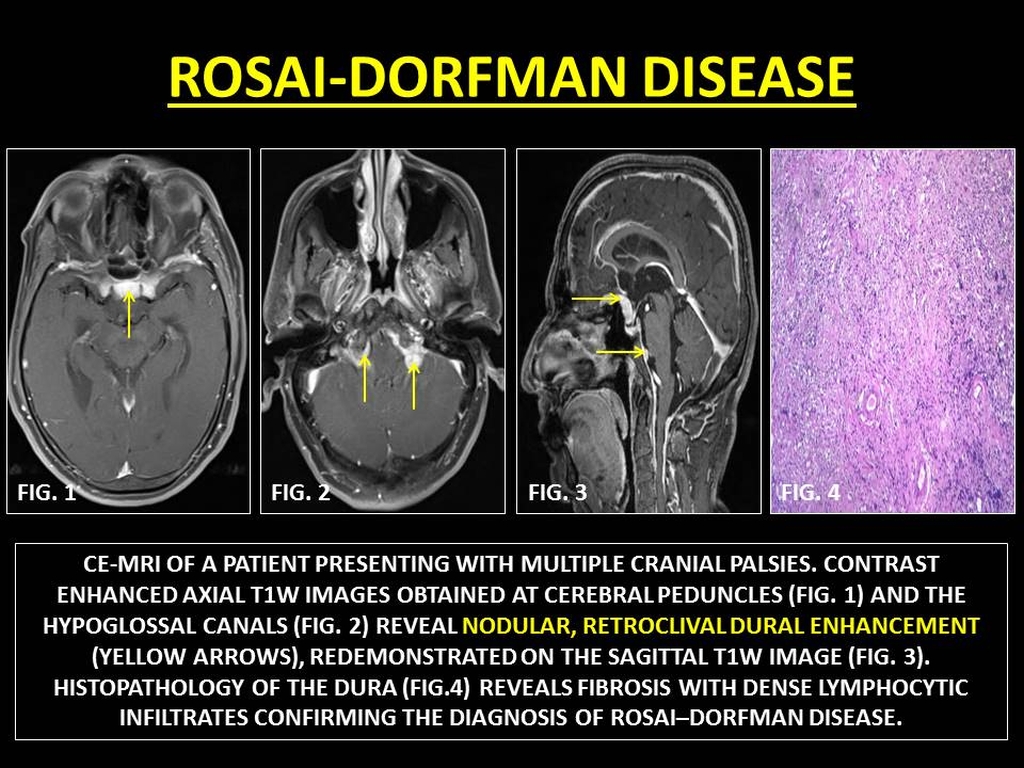
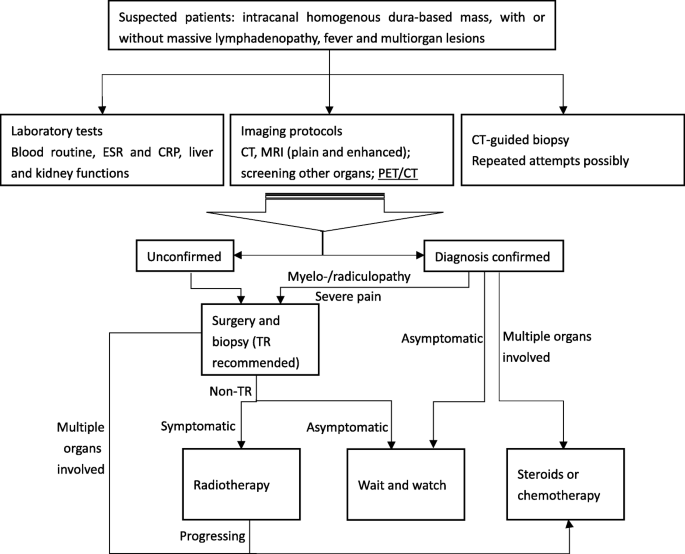
Rosai-Dorfman disease RD also known as sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy SHML is a rare histiocytic disorder which involves the over-production of a type of white blood cell called non Langerhans sinus histiocyte. Rosai-Dorfman disease RDD is a sporadic idiopathic sinus histiocytosis plausibly reactive in nature and well responsive to pharmacological and surgical treatment. Central nervous system involvement is extremely rare particularly cases with multiple intracranial masses.
These histiocytes most often accumulate in the nodes in the neck cervical nodes though other lymph nodes and other parts of the body may also be affected. These incorrect signals are caused by changes in genes mutations that lead to tissue damage lesions which causes disease.
Rosai-Dorfman-Destombes disease RDD is a rare histiocytic disorder described by Destombes in 1965 and later by Rosai and Dorfman in 1969 as sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy and previously classified by the Working Group of the Histiocyte Society of 1987 as a non-Langerhans cell LC histiocytosis.
Though it can affect almost any organ system involvement of the nervous system is exceedingly rare. Although it is characterized by unique indeed pathognomonic histopathological cytoarchitecture it may be mistaken for many other neoplastic and inflammatory histioproliferative diseases. Rosai-Dorfman disease is a rare disorder characterized histologically by lymphatic sinus dilatation due to histiocyte proliferation. Rosai-Dorfman disease was first described by Rosai and Dorfman in 1969. It is usually characterized by cervical lymphadenopathy along with systemic features. In the central nervous system Rosai-Dorfman disease is ubiquitous. Rosai-Dorfman-Destombes disease RDD is a rare histiocytic disorder described by Destombes in 1965 and later by Rosai and Dorfman in 1969 as sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy and previously classified by the Working Group of the Histiocyte Society of 1987 as a non-Langerhans cell LC histiocytosis. The phenotype of Faisalabad histiocytosis overlaps with that of Rosai-Dorfman disease RDD or sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy SHML a histiocytic disorder characterized by painless but protracted lymphadenopathy with lymph node histology showing large histiocytes with voluminous clear cytoplasm rounded nuclei and emperipolesis. Our goal was to describe the CT MRI and 18F-FDG FD.
In the central nervous system Rosai-Dorfman disease is ubiquitous. Rosai-Dorfman disease is a rare disorder characterized histologically by lymphatic sinus dilatation due to histiocyte proliferation. Our goal was to describe the CT MRI and 18F-FDG FD. Rosai-Dorfman disease RDD first described in 1969 is a disease that occurs when the body produces too many histiocytes in the lymph nodes. Though it can affect almost any organ system involvement of the nervous system is exceedingly rare. It is a benign disease which is characterized by over-production and accumulation of a specific type of white blood cell histiocyte in the lymph nodes of the body most often those of the neck cervical. The phenotype of Faisalabad histiocytosis overlaps with that of Rosai-Dorfman disease RDD or sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy SHML a histiocytic disorder characterized by painless but protracted lymphadenopathy with lymph node histology showing large histiocytes with voluminous clear cytoplasm rounded nuclei and emperipolesis.






























Post a Comment for "Rosai Dorfman Disease Brain"